You are here
Diseases Treated
This website was the first in 2003 to sort diseases treated with cord blood into 3 categories:
Before choosing the right form of cord blood banking it is also important to distinguish between two modes of treatment:
- Allogeneic - patient receives stem cells from a matching donor, either a sibling or an unrelated donor
- Autologous - patient receives their own stem cells
When parents donate cord blood to a public bank, they are supporting patients around the world who are searching for an unrelated Allogeneic donor. When parents save cord blood in a family bank, they are reserving the options that the baby can use its own stem cells for an Autologous treatment, or an immediate relative (sibling or parents) can use the stem cells for an Allogeneic treatment.
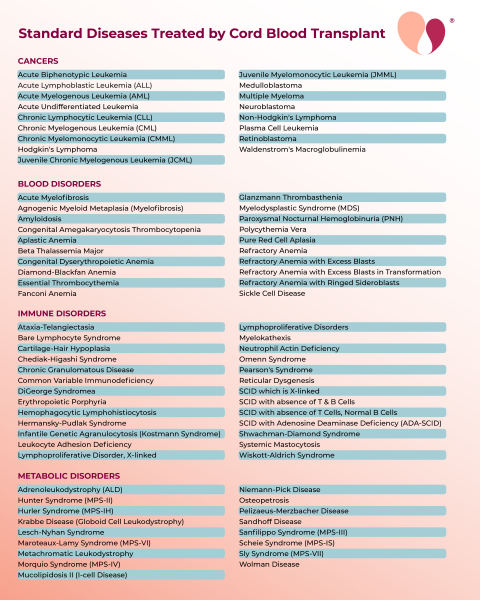
Here is a one page list of the roughly 80 standard therapies.
Standard Therapies with blood-forming stem cells
These are diseases for which transplants of blood-forming stem cells (Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplants, HSCT) are a standard treatment. For some diseases they are the only therapy, and in other diseases they are only employed when front-line therapies have failed or the disease is very aggressive. The lists below include ALL therapies that use blood-forming stem cells, without distinction as to whether the stem cells were extracted from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or cord blood. In the United States, most health insurance providers will pay for a stem cell transplant if it is a "standard therapy" for the patient's diagnosis.
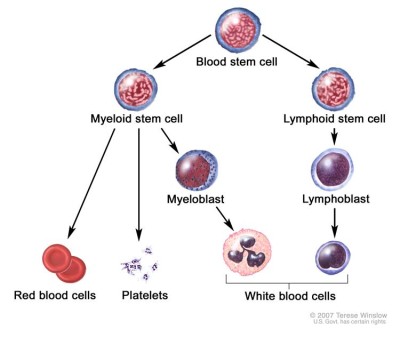
Most of the diseases for which HSCT is a standard treatment are disorders of blood cell lineage. The proliferation by which blood cells are formed from stem cells is illustrated in the side graphic (click on the image to expand it).
Leukemia is a cancer of the blood immune system, where the cells are called leukocytes or white cells
| Diagnosis | Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Autologous (Own Cells) |
| Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) | ✔ | |
| Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) | ✔ | |
| Acute Biphenotypic Leukemia | ✔ | |
| Acute Undifferentiated Leukemia | ✔ | |
| Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) | ✔ | |
| Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) | ✔ | |
| Juvenile Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (JCML) | ✔ | |
| Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) | ✔ |
Myelodysplastic Syndromes are also called pre-leukemia
| Diagnosis | Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Autologous (Own Cells) |
| Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) | ✔ | |
| Refractory Anemia | ✔ | |
| Refractory Anemia with Ringed Sideroblasts (Sideroblastic anemia) | ✔ | |
| Refractory Anemia with Excess Blasts | ✔ | |
| Refractory Anemia with Excess Blasts in Transformation | ✔ | |
| Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML) | ✔ |
Lymphoma is a cancer of the leukocytes that circulate in the blood and lymph vessels
| Diagnosis | Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Autologous (Own Cells) |
| Hodgkin's Lymphoma | ✔ | ✔ |
| Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (Burkitt's Lymphoma) | ✔ |
Other Disorders of Blood Cell Proliferation
| Diagnosis | Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Autologous (Own Cells) |
| Anemias are deficiencies or malformations of red cells: | ... | ... |
| Aplastic Anemia | ✔ | ✔ |
| Fanconi Anemia (The first cord blood transplant in 1988 was for FA, an inherited disorder) | ✔ | |
| Congenital Dyserythropoietic Anemia | ✔ | |
| Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH) | ✔ | |
| Inherited Red Cell Abnormalities Red cells contain hemoglobin and carry oxygen to the body: | ... | ... |
| Sickle Cell Disease | ✔ | |
| Beta Thalassemia Major (aka Cooley's Anemia) | ✔ | |
| Diamond-Blackfan Anemia | ✔ | |
| Pure Red Cell Aplasia | ✔ | |
| Inherited Platelet Abnormalities Platelets are blood cells needed for clotting: | ... | ... |
| Amegakaryocytosis / Congenital Thrombocytopenia | ✔ | |
| Glanzmann Thrombasthenia | ✔ | |
| Inherited Immune System Disorders: Severe Combined Immunodeficiency(SCID) | ... | ... |
| SCID with Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency (ADA-SCID) | ✔ | |
| SCID which is X-linked | ✔ | |
| SCID with absence of T & B Cells | ✔ | |
| SCID with absence of T Cells, Normal B Cells | ✔ | |
| Omenn Syndrome | ✔ | |
| Inherited Immune System Disorders: Neutropenias | ... | ... |
| Infantile Genetic Agranulocytosis (Kostmann Syndrome) | ✔ | |
| Myelokathexis | ✔ | |
| Inherited Immune System Disorders: Other | ... | ... |
| Ataxia-Telangiectasia | ✔ | |
| Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome | ✔ | |
| Common Variable Immunodeficiency | ✔ | |
| DiGeorge Syndrome | ✔ | |
| Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis | ✔ | |
| Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency | ✔ | |
| Lymphoproliferative Disorders | ✔ | |
| Lymphoproliferative Disorder, X-linked (Susceptibility to Epstein-Barr virus) | ✔ | |
| Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome | ✔ | |
| Myeloproliferative Disorders: | ... | ... |
| Acute Myelofibrosis | ✔ | |
| Agnogenic Myeloid Metaplasia (Myelofibrosis) | ✔ | |
| Polycythemia Vera | ✔ | |
| Essential Thrombocythemia | ✔ | |
| Phagocyte Disorders These are immune system cells that engulf and kill foreign organisms: | ... | ... |
| Chediak-Higashi Syndrome | ✔ | |
| Chronic Granulomatous Disease | ✔ | |
| Neutrophil Actin Deficiency | ✔ | |
| Reticular Dysgenesis | ✔ | |
| Bone Marrow Cancers: | ... | ... |
| Multiple Myeloma | ✔ | ✔ |
| Plasma Cell Leukemia | ✔ | ✔ |
| Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia | ✔ | ✔ |
Transplants for Inherited Disorders of the Immune System & Other Organs
| Diagnosis | Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Autologous (Own Cells) |
| Cartilage-Hair Hypoplasia | ✔ | |
| Erythropoietic Porphyria | ✔ | |
| Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome | ✔ | |
| Pearson's Syndrome | ✔ | |
| Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome | ✔ | |
| Systemic Mastocytosis | ✔ |
Transplants for Inherited Metabolic Disorders
| Diagnosis | Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Autologous (Own Cells) |
| Amyloidosis | ✔ | |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) Storage Diseases: | ... | ... |
| Hurler Syndrome (MPS-IH) | ✔ | |
| Scheie Syndrome (MPS-IS) | ✔ | |
| Hunter Syndrome (MPS-II) | ✔ | |
| Sanfilippo Syndrome (MPS-III) | ✔ | |
| Morquio Syndrome (MPS-IV) | ✔ | |
| Maroteaux-Lamy Syndrome (MPS-VI) | ✔ | |
| Sly Syndrome (MPS-VII) (beta-glucuronidase deficiency) | ✔ | |
| Mucolipidosis II (I-cell Disease) | ✔ | |
| Leukodystrophy Disorders: | ... | ... |
| Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) | ✔ | |
| Krabbe Disease(Globoid Cell Leukodystrophy) | ✔ | |
| Metachromatic Leukodystrophy | ✔ | |
| Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease | ✔ | |
| Lysosomal Storage Diseases: | ... | ... |
| Niemann-Pick Disease | ✔ | |
| Sandhoff Disease | ✔ | |
| Wolman Disease | ✔ | |
| Other Inherited Metabolic Disorders: | ... | ... |
| Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome | ✔ | |
| Osteopetrosis | ✔ |
Solid tumors not originating in the blood or immune system
| Diagnosis | Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Autologous (Own Cells) |
| Neuroblastoma | ✔ | |
| Medulloblastoma | ✔ | |
| Retinoblastoma | ✔ |
Diseases and Disorders that have been in Clinical Trials with Cord Blood or Cord Tissue Cells
A "clinical trial" is a study in human patients for an emerging therapy that has not been adopted as standard therapy. This website has pages that enable patients to search worldwide for currently recruiting clinical trials with either cord blood or umbilical cord tissue MSC. The table below checks off all diagnoses that have ever been treated in clinical trials with cord blood or cord tissue, regardless of whether the trials are still open.
The phases of U.S. clinical trials in humans are defined as follows (in other countries phases may be different):
- Phase 1: Safety study to see if the procedure or drug is well-tolerated.
- Phase 2: Larger study to measure effectiveness of the new treatment against a control group.
- Phase 3: Even larger study to compare the effect of various parameters such as dose and administration, and to monitor side effects prior to market release.
- Phase 4: Post-marketing studies to learn even more about risks, benefits, and optimal use.
Neurologic Disorder
| Diagnosis | Cord Blood Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Cord Blood Autologous (Own Cells) | Cord Tissue Allogeneic (Donor Cells) |
| Alzheimer's disease | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Autism | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Cerebral Palsy | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Encephalopathy | ✔ | ||
| Global Developmental Delay | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Hearing Loss (acquired sensorineural) | ✔ | ||
| Intraventricular Hemorrhage | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Parkinson's disease | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Spinal Cord Injury | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Stroke | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Traumatic Brain Injury | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
Auto-Immune Disorders
| Diagnosis | Cord Blood Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Cord Blood Autologous (Own Cells) | Cord Tissue Allogeneic (Donor Cells) |
| Alopecia Areata | ✔ | ||
| Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Crohn's Disease | ✔ | ||
| Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) | ✔ | ||
| Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Lupus | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Multiple Sclerosis | ✔ | ||
| Psoriasis | ✔ | ||
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Scleroderma | |||
| Systemic Sclerosis | ✔ | ||
| Ulcerative Colitis | ✔ |
Cardiovascular
| Diagnosis | Cord Blood Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Cord Blood Autologous (Own Cells) | Cord Tissue Allogeneic (Donor Cells) |
| Acute Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack) | ✔ | ||
| Cardiomyopathy | ✔ | ||
| Critical Limb Ischemia (CLI) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Heart Failure | ✔ | ||
| Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Surgery for Congenital Heart Defects | ✔ |
Diabetic
| Diagnosis | Cord Blood Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Cord Blood Autologous (Own Cells) | Cord Tissue Allogeneic (Donor Cells) |
| Diabetes, Type 1 (this is Auto-Immune) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Diabetes, Type 2 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Diabetic Foot Ulcer | ✔ | ||
| Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy | ✔ |
Genetic and/or Metabolic Disorders
| Diagnosis | Cord Blood Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Cord Blood Autologous (Own Cells) | Cord Tissue Allogeneic (Donor Cells) |
| Aging Frailty | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy | ✔ | ||
| Epidermolysis Bullosa | ✔ | ||
| Hereditary Ataxia | ✔ | ||
| Lysosomal Storage Diseases | ✔ | ||
| Metabolic Syndrome | ✔ | ||
| Severe Combined Immunodeficiency | ✔ | ||
| Spinal muscular atrophy | ✔ | ||
| Tay-Sachs Disease | ✔ |
Orthopedic
| Diagnosis | Cord Blood Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Cord Blood Autologous (Own Cells) | Cord Tissue Allogeneic (Donor Cells) |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis | ✔ | ||
| Cartilage Injury | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Cleft Palate Repair | ✔ | ||
| Non-Union Fractures | ✔ | ||
| Osteoarthritis | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Osteochondral Lesion | ✔ | ||
| Spinal Fusion Surgery | ✔ |
Other
| Diagnosis | Cord Blood Allogeneic (Donor Cells) | Cord Blood Autologous (Own Cells) | Cord Tissue Allogeneic (Donor Cells) |
| Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) | ✔ | ||
| BronchoPulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) (lung disorder due to premature birth) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Erectile Dysfunction | ✔ | ||
| Eye Diseases | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Fistula | ✔ | ||
| HIV | ✔ | ||
| Kidney Failure | ✔ | ||
| Liver Cirrhosis | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Liver Failure | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Peyronie's Disease | ✔ | ||
| Premature Ovarian Failure | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Uterine Scars | ✔ | ||
| Wounds | ✔ |
Experimental Treatments
These are diagnoses for which stem cell treatments are being studied either in the laboratory with cell cultures or in animals that mimic the human disease. The experimental therapies are not yet in human clinical trials. In experimental research, it is often not clear whether an eventual therapy, if developed, would be Autologous or Allogeneic. Due to the explosion of stem cell research and the difficulty keeping track of which studies are promising, this section does not have a list.