Usted está aquí
HEMAFUND CorD Program
 HEMAFUND (ГЕМАФОНД) is a family cord blood bank in Kyiv, Ukraine, that was set up by Yaroslav Issakov in 2005. By now the entity houses biotechnical and clinical diagnostic laboratories and a cryobank with more than 26 000 samples stored.
HEMAFUND (ГЕМАФОНД) is a family cord blood bank in Kyiv, Ukraine, that was set up by Yaroslav Issakov in 2005. By now the entity houses biotechnical and clinical diagnostic laboratories and a cryobank with more than 26 000 samples stored.
Alongside private cord blood preservation, mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) from umbilical cord, placenta and pericardium, since 2009 HEMAFUND has been implementing a charitable project called “Ukraine-wide application of the cord blood program.” Within this programme HEMAFUND is providing support for Ukrainian families, medical clinics, and academics who wish to apply cord blood for different conditions such as congenital heart defects and birth defects which can be fixed by surgery, as well as anaemia of the newborn.
Since then HEMAFUND has become a world leader in the provision of cord blood for newborns who require surgery within hours of birth. Since 2009, more than 360 newborns have had operations supported with cord blood and their lives were saved with the help of HEMAFUND and their medical institution partners, namely:
- Scientific-Practical Medical Center of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery,
- Kiev city delivery hospital №5
- Perinatal Center of Kiev
- Institute of Pediatrics, Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Romodanov Institute of Neurosurgery
- National Children's Specialized Hospital Okhmatdit
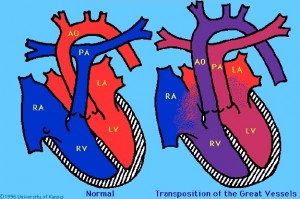 In Ukraine, the incidence of congenital heart defects is 4-5% among newborns, significantly higher than in the United States (CDC, AHA). A heart defect is considered "critical" if the baby will require surgery within the first year of life. An example of such a defect is Transposition of Great Arteries, known as D-TGA, illustrated at left. In a given year, the Ukraine sees 700-900 children born with complex critical congenital heart defects and 150-200 children born with a defect of the neural tube (spina bifida). Many of these children have the possibility to live fairly normal lives if their defects are corrected within hours of birth.
In Ukraine, the incidence of congenital heart defects is 4-5% among newborns, significantly higher than in the United States (CDC, AHA). A heart defect is considered "critical" if the baby will require surgery within the first year of life. An example of such a defect is Transposition of Great Arteries, known as D-TGA, illustrated at left. In a given year, the Ukraine sees 700-900 children born with complex critical congenital heart defects and 150-200 children born with a defect of the neural tube (spina bifida). Many of these children have the possibility to live fairly normal lives if their defects are corrected within hours of birth.
The CorD program organized by Scientific-Practical Medical Center of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery lead by Prof. Ilya Yemets, MD PhD, and supported by HEMAFUND, is groundbreaking. The program makes it possible to identify children with serious birth defects in utero, arrange to collect their cord blood at birth, and rush the children to surgery supported by cord blood within hours of birth.
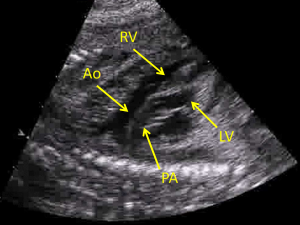 For a baby with a congenital heart defect, the journey through the CorD program starts at diagnosis. Several studies have reported better patient outcomes with prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease. Children in the CorDi program were diagnosed by foetal echocardiography between the 22nd and 28th week of gestation and this was confirmed at the 36th week. Mothers underwent health examination and informed consent. Contraindications for the use of autologous cord blood during foetal surgery would be a blood type incompatibility between the mother and baby, or the presence of infection.
For a baby with a congenital heart defect, the journey through the CorD program starts at diagnosis. Several studies have reported better patient outcomes with prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease. Children in the CorDi program were diagnosed by foetal echocardiography between the 22nd and 28th week of gestation and this was confirmed at the 36th week. Mothers underwent health examination and informed consent. Contraindications for the use of autologous cord blood during foetal surgery would be a blood type incompatibility between the mother and baby, or the presence of infection.
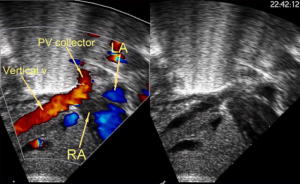
Images on the side of this article illustrate the case of a baby boy, one of twins, who was diagnosed with D-TGA plus additional complications and was successfully treated in the CorDi program. The first foetal echocardiogram was taken at 23 weeks gestation and the second was taken at 1 hour after birth.
The date of delivery was planned so that all equipment and staff would be in place to rescue the baby. Immediately after delivery of the newborn, in the first 10 seconds, the umbilical cord was double clamped and cut as close as possible to the abdomen of the baby. A specially trained team collected the umbilical cord blood in accordance with the 4th edition of the FACT-NetCord Standards. Irrespective of the type of delivery (vaginal or cesarean section) the cord blood was harvested “in utero”, prior to delivery of the placenta. The volume of anticoagulant CPD in the collection bag was adjusted to a ratio of 1ml per 5ml of blood.
 To maximize the volume of cord blood harvested, the umbilical vein was punctured up to three times, of course with each puncture accompanied by clamping and the use of sterile technique. A small volume of cord blood was used to test for ABO-Rh blood type, conduct aerobic and anaerobic bacterial culturing, and check for HIV. The main cord blood collection bag and two satellite bags were transported to the surgical suite in a mobile refrigerator set to 4°C temperature.
To maximize the volume of cord blood harvested, the umbilical vein was punctured up to three times, of course with each puncture accompanied by clamping and the use of sterile technique. A small volume of cord blood was used to test for ABO-Rh blood type, conduct aerobic and anaerobic bacterial culturing, and check for HIV. The main cord blood collection bag and two satellite bags were transported to the surgical suite in a mobile refrigerator set to 4°C temperature.
Simultaneously, upon birth the baby was rushed to Ukraine Children’s Cardiac Center by ambulance, arriving within 40-60 minutes after birth. Before surgery, babies were examined by echocardiography and brain MRI (to exclude perinatal brain injury that might confuse measurements of the response to the cardiac surgery). The pre-surgery imaging not only confirms the initial diagnosis but helps the surgeons to visualize any additional anomalies in advance. To avoid any clerical mistakes, the blood type of the baby and the cord blood unit were cross-matched before surgery.
 Open heart surgery to correct congenital defects requires cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) of the blood supply, and whole umbilical cord blood was used to supply additional blood volume for the extracorporeal circuit of the heart-lung machine. Autologous cord blood (AUCB) is the ideal supplement to the baby’s blood, to avoid numerous immunological and non-immunological complications that can result from blood transfusions. Moreover, publications report that AUCB has properties that are advantageous to neonatal open heart surgery: high level of growth factors, higher oxygen affinity of foetal haemoglobin, presence of stem cells, and harmless collection procedure. The CorD approach prevents transfusion associated diseases, alloimmunization, consequent risks of transfusion reactions, and reduces demand on donor blood.
Open heart surgery to correct congenital defects requires cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) of the blood supply, and whole umbilical cord blood was used to supply additional blood volume for the extracorporeal circuit of the heart-lung machine. Autologous cord blood (AUCB) is the ideal supplement to the baby’s blood, to avoid numerous immunological and non-immunological complications that can result from blood transfusions. Moreover, publications report that AUCB has properties that are advantageous to neonatal open heart surgery: high level of growth factors, higher oxygen affinity of foetal haemoglobin, presence of stem cells, and harmless collection procedure. The CorD approach prevents transfusion associated diseases, alloimmunization, consequent risks of transfusion reactions, and reduces demand on donor blood.
 HEMAFUND provides all handling and delivery of umbilical cord blood for the CorD program. According to the cardiac surgeons, the stem cells contained in the umbilical cord blood significantly accelerate the post-operative recovery of the patients. The results of CorD turned out to be so effective that the methodology became official protocol of use in Ukraine (Order of the Ministry of Healthcare of Ukraine #764 from 01.10.2012) and in other countries. Currently, “Ukraine-wide application of the cord blood program” is actively developing and overseeing the development of new techniques for the effective use of umbilical cord blood.
HEMAFUND provides all handling and delivery of umbilical cord blood for the CorD program. According to the cardiac surgeons, the stem cells contained in the umbilical cord blood significantly accelerate the post-operative recovery of the patients. The results of CorD turned out to be so effective that the methodology became official protocol of use in Ukraine (Order of the Ministry of Healthcare of Ukraine #764 from 01.10.2012) and in other countries. Currently, “Ukraine-wide application of the cord blood program” is actively developing and overseeing the development of new techniques for the effective use of umbilical cord blood.
In an effort to develop more ways to help children with cardiac defects, HEMAFUND has collaborated with the Research Department of the Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery hospital to develop a technique that cryopreserves the pericardium that surrounds the heart. The cryopreserved pericardium is intended to replace grafts made from synthetic materials or animal organs for the reconstruction of congenital heart defects in children.
Table of Cardiac Patients in HEMAFUND CorD Program
| Number Patients | Diagnosis | Cardiac Surgery | Birth Weight (kg) (mean ± std. dev.) | Cord Blood Volume (mL) (mean ± std. dev.) |
| 129 | TGA, IVS | ASO | 3.45 ± 0.5 | 85 ± 24 |
| 1 | TGA,TAPVC | ASO, TAPVC repair | 2.5 | 80 |
| 1 | Taussig-Bing anomaly, IAA | ASO, VSD repair, aortic arch repair | 2.95 | 70 |
| 1 | Ebstein’s anomaly | Ebstein’s repair | 3.06 | 75 |
| 1 | Ebstein’s anomaly, PA I | Ebstein’s repair; valvuloplasty, pulmonic | 3.29 | 86 |
| 1 | APW, IAA | APW repair, aortic arch repair | 2.2 | 67 |
| 1 | Tumor in LVOT | LVOTO procedure | 3.3 | 70 |
| 1 | Truncus Arteriosus | Truncus Arteriosus repair | 3.0 | 80 |
| 38 | Others* | Off pump surgeries | 3.0 ± 0.5 | 70 ± 35 |
Table Legend:
TGA: transposition of the great arteries; VSD: ventricular septal defect; TAPVC: total anomalous pulmonary venous communication; IAA: interruption of the aortic arch; PA: pulmonary atresia; APW: aortopulmonary window; ASO: arterial switch operation; LVOTO: Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction; UCB: umbilical cord blood; CPB: cardiopulmonary bypass; *Coarctation of the Aorta, Single ventricle with the first stage of palliative surgery (e.g. RMBTSH)
In addition, HEMAFUND supported the initiative to create a public bank of umbilical cord blood “Bank of Life” (Банк Життя). The ambitious task of its management team to is to build an inventory of 24 000 cord blood units to meet the needs of stem cell transplant patients in Ukraine and beyond.
Publications:
- Fedevych, O., Chasovskyi, K., Vorobiova, G., Zhovnir, V., Makarenko, M., Kurkevych, A., Maksymenko, A. and Yemets, I., 2011. Open cardiac surgery in the first hours of life using autologous umbilical cord blood. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, 40(4), pp.985-989. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2011.01.011
- Chasovskyi, K., Fedevych, O., Vorobiova, G., Zhovnir, V., Maksimenko, A., Boychenko, O., Lysak, Y., Cohen, G. and Yemets, I., 2012. Arterial switch operation in the first hours of life using autologous umbilical cord blood. The Annals of thoracic surgery, 93(5), pp.1571-1576. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.01.104
- Chasovskyi, K. and Yemets, I., 2015. Impact of carbon dioxide tension during cardiopulmonary bypass on tissue perfusion in neonates undergoing cardiac surgery using autologous umbilical cord blood. Perfusion, p.0267659115624004. doi: 10.1177/0267659115624004
- Chasovskyi, K., Fedevych, O., McMullan, D.M., Mykychak, Y., Vorobiova, G., Zhovnir, V. and Yemets, I., 2015. Tissue perfusion in neonates undergoing open-heart surgery using autologous umbilical cord blood or donor blood components. Perfusion, 30(6), pp.499-506. doi: 10.1177/0267659114550234