現在地
FamiCord has released over 7550 stem cell therapies
FamiCord is not just a cord blood bank
The FamiCord Group has the largest cord blood bank network in Europe, and extends to the Middle East as well. As of June 2025, the FamiCord Group owns the majority share of 13 cord blood laboratories in 10 countries1. Taking advantage of its presence in multiple countries, operating laboratories under multiple regulatory environments, FamiCord has been able to provide therapies with a wide variety of stem cell types. Famicord has also provided a wide range of stem cell treatments that include both standard hospital care as well as experimental research.
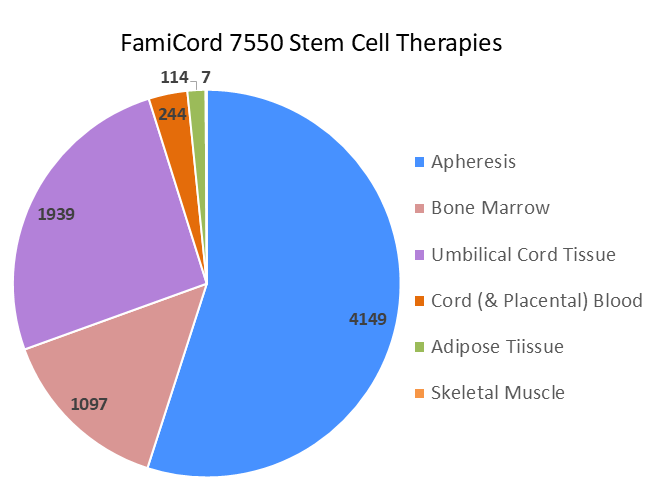
FamiCord has a commitment to fostering therapies with stem cells, not only banking cells. By May of 2025, the FamiCord list of therapeutic applications included 7550 stem cell therapies. In the pie chart above, we display these therapies by stem cell type. Over half (55%) of the released therapies are mobilized peripheral blood (apheresis) for stem cell transplants. These include both autologous and allogeneic transplants. Another 14.5% of the releases are bone marrow stem cells for transplants, from both related and unrelated donors. FamiCord has a very active program collecting donated umbilical cord tissue and processing it to culture mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) for therapies in clinical trials and Hospital Exemption (HE) programs2. These accounted for 25.7% of released therapies. Similarly, Famicord has supplied MSC from adipose tissue for therapies (1.5%) in clinical trials and HE programs. The cord blood releases, both standard transplants and regenerative medicine, are only 3.2% of the total FamiCord therapies. Lastly, a small number of stem cells from skeletal muscle were processed as a contract manufacturer for a clinical trial of a novel therapy.
Timeline of cord blood units released
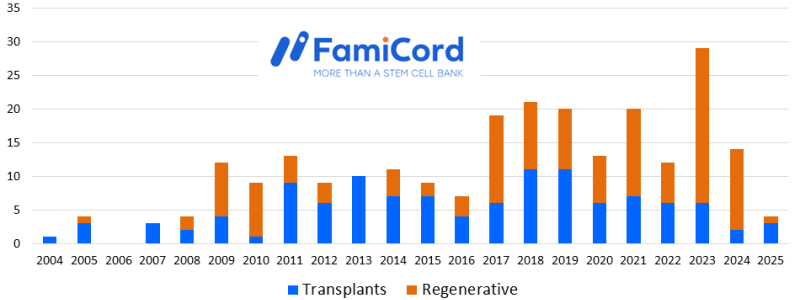
The total number of FamiCord therapies with cord blood and/or placental blood is 244 as of May 2025. These releases went to standard stem cell transplants in 117 (48%) of the cases and to regenerative medicine in the other 127 (52%). The timeline below shows the number of releases per year. Bear in mind that all cord blood banks experienced some slow-down in releasing therapies during the Coronavirus pandemic, and that impact is more noticeable when the releases are plotted annually rather than cumulatively.
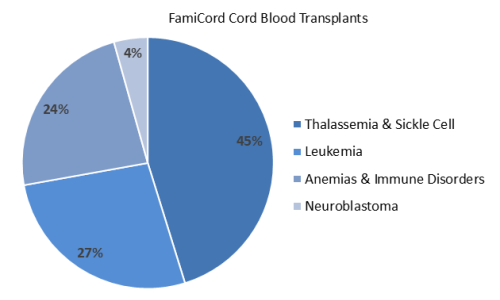
Indications for releases
The next two pie charts show the breakdown of cord blood releases by indication for both the transplants and the regenerative medicine therapies.
The pie chart of transplants by diagnosis shows that the most common indications for FamiCord releases have been inherited blood disorders such as Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Disease (45%), followed by blood cancers (27%). This is similar to the pattern seen in releases from the largest family cord blood banks in the USA: CBR had 50% of transplants for blood disorders such as hemoglobinopathies, followed by 39% for cancers such as leukemia; ViaCord had 49% hemoglobinopathies and 42% for oncology and bone marrow failure.
The pie chart of indications for regenerative medicine releases is dominated by brain injuries (51%) and neurodevelopment disorders (43%). This is similar to the pattern seen in releases from the largest family cord blood banks in the USA: CBR had 53% of regenerative medicine for brain injuries, followed by 44% for developmental disorders; ViaCord had 97.5% for these two categories combined.

A big difference between FamiCord and cord blood banks in the USA is that cord blood regenerative therapies are free for FamiCord clients. Whereas USA banks partner with Duke University, which charges fees to patients, FamiCord is partnered with Lublin University Children’s Hospital to facilitate its clients access to cord blood therapy for cerebral palsy or autism. For parents that have not stored cord blood with FamiCord, MSC therapies for neurodevelopmental conditions can be available and financed through non-profit fund-raising
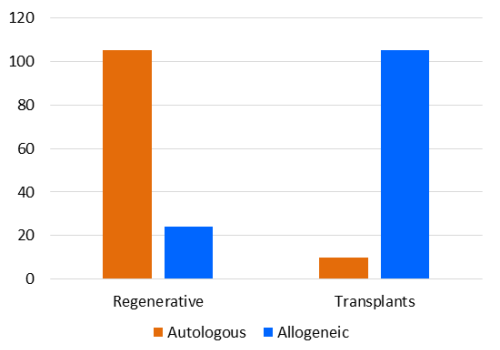
Autologous versus Allogeneic use
It is of interest to compare how many patients were treated with their own cord blood (autologous) versus cord blood from a donor (allogeneic). In regenerative medicine, 83% of the releases were autologous, whereas among the standard transplants the releases were 91% allogeneic.
In some countries, FamiCord collects cord blood donations for public and hybrid banking. As a result, the FamiCord cord blood therapies that came from donors (allogeneic) were not always from a sibling of the patient. Among the cord blood transplants, 13 of the 107 (12%) allogeneic therapies were from an unrelated donor. Among the regenerative medicine treatments, 4 of the 22 (18%) allogeneic therapies were from an unrelated donor.
The FamiCord experience demonstrates that having a wide range of laboratory operations creates more opportunities for providing therapies, not just banking of stem cells.
References
- Baran T. The story behind FamiCord becoming the largest cord blood bank in Europe. Parent's Guide to Cord Blood Foundation Newsletter Published 2022-10
- Verter F. FamiCord: Europe’s largest cord blood bank and largest manufacturer of cord tissue MSC therapy. Parent's Guide to Cord Blood Foundation Newsletter Published 2018-10